Configure OpenELB for Multi-router Clusters (BGP Mode)
This document describes how to configure OpenELB in BGP mode for Kubernetes cluster nodes deployed under multiple routers.
NOTE
Network Topology
This section describes the configuration result you need to achieve. The following figure shows the network topology of a Kubernetes cluster after the configuration.
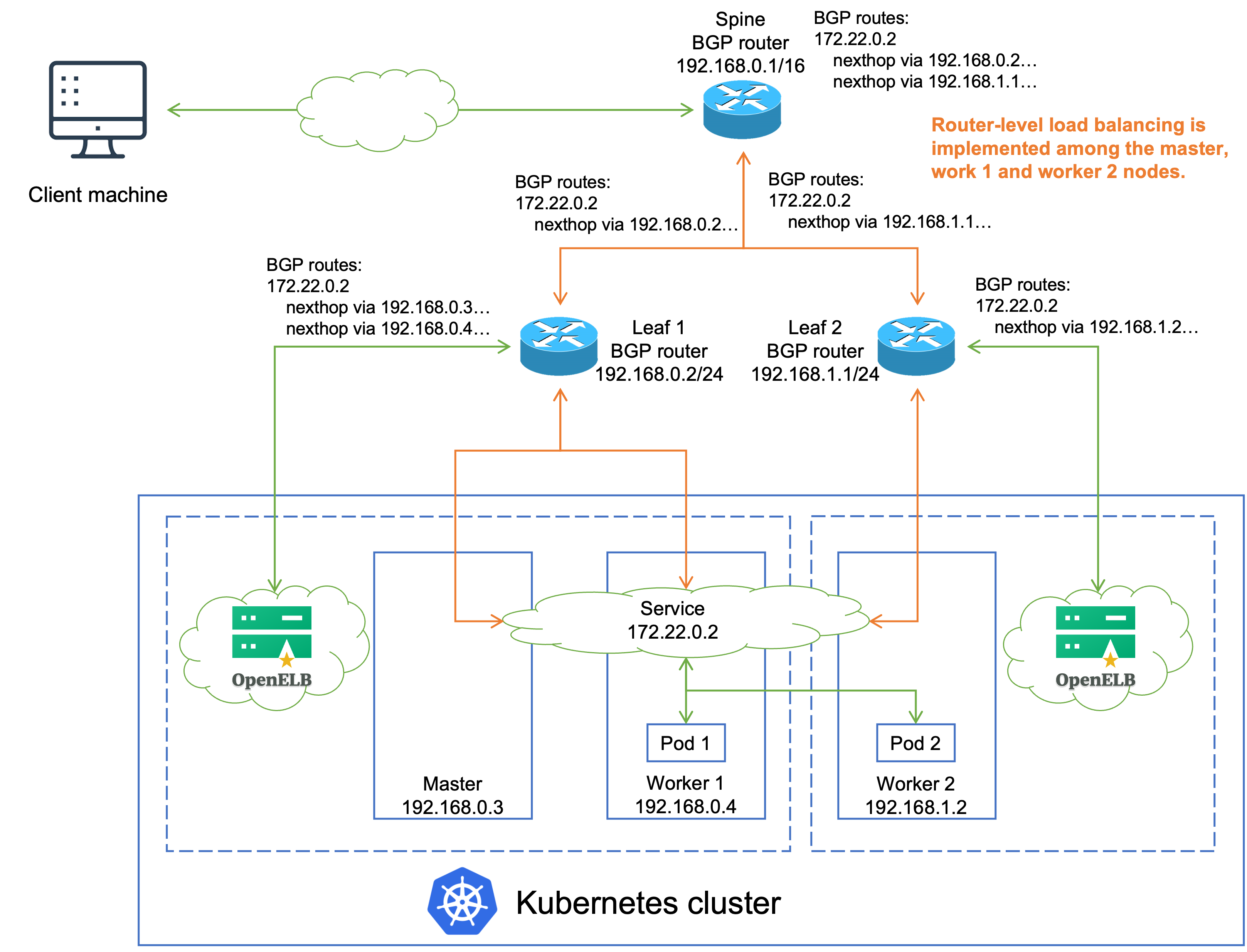
IP addresses in the preceding figure are examples only. The topology is described as follows:
- In the Kubernetes cluster, the master and worker 1 nodes are deployed under the leaf 1 BGP router, and the worker 2 node is deployed under the leaf 2 BGP router. OpenELB is installed on nodes under all leaf routers.
- A Service backed by two Pods is deployed in the Kubernetes cluster, and is assigned an IP address 172.22.0.2 for external access. Pod 1 and Pod 2 are deployed on worker 1 and worker 2 respectively.
- The OpenELB replica installed under leaf1 establishes a BGP connection with leaf 1 and publishes the IP addresses of the master node and worker 1 (192.168.0.3 and 192.168.0.4) to leaf 1 as the next hop destined for the Service IP address 172.22.0.2.
- The OpenELB replica installed under leaf 2 establishes a BGP connection with leaf 2 and publishes the worker 2 IP address 192.168.1.2 to leaf 2 as the next hop destined for the Service IP address 172.22.0.2.
- Leaf 1 establishes a BGP connection with the spine BGP router and publishes its own IP address 192.168.0.2 to the spine router as the next hop destined for the Service IP address 172.22.0.2.
- Leaf 2 establishes a BGP connection with the spine router and publishes its own IP address 192.168.1.1 to the spine router as the next hop destined for the Service IP address 172.22.0.2.
- When an external client machine attempts to access the Service, the spine router load balances the Service traffic among leaf 1 and leaf 2. Leaf 1 load balances the traffic among the master node and worker 1. Leaf 2 forwards the traffic to worker 2. Therefore, the Service traffic is load balanced among all three Kubernetes cluster nodes, and the Service bandwidth of all three nodes can be utilized.
Configuration Procedure
Prerequisites
You need to prepare a Kubernetes cluster where OpenELB has been installed.
Procedure
NOTE
-
Log in to the Kubernetes cluster and run the following commands to label the Kubernetes cluster nodes where openelb-speaker is to be scheduled:
kubectl label --overwrite nodes master1 worker-p002 lb.kubesphere.io/v1alpha1=openelbNOTE
OpenELB works properly if it is installed on only one node under each leaf router. In this example, OpenELB will be installed on master1 under leaf1 and worker-p002 under leaf2. However, to ensure high availability in a production environment, you are advised to installed OpenELB on at least two nodes under each leaf router. -
Run the following command to edit the openelb-speaker DaemonSet:
kubectl edit ds openelb-speaker -n openelb-system -
In the openelb-speaker DaemonSet YAML configuration, add the following fields under
spec:template:spec:nodeSelector: kubernetes.io/os: linux lb.kubesphere.io/v1alpha1: openelb -
Run the following commands to label the Kubernetes cluster nodes so that the openelb-speaker instances establish BGP connections with the correct BGP routers.
kubectl label --overwrite nodes master1 openelb.kubesphere.io/rack=leaf1 kubectl label --overwrite nodes worker-p002 openelb.kubesphere.io/rack=leaf2 -
When creating BgpPeer objects, configure the spec:nodeSelector:matchLabels field in the BgpPeer YAML configuration for each leaf router. The following YAML configurations specify that the OpenELB replica on master1 communicates with leaf1, and the OpenELB replica on worker-p002 communicates with leaf2.
# BgpPeer YAML for master1 and leaf1 nodeSelector: matchLabels: openelb.kubesphere.io/rack: leaf1# BgpPeer YAML for worker-p002 and leaf2 nodeSelector: matchLabels: openelb.kubesphere.io/rack: leaf2
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.